Why Data Democratization matters?
Most of the data that companies are creating or collecting today is unused, even though it is widely viewed as a strategic asset. To exploit this data and create value from it, an increasing number of employees besides data experts need to access and work with data in an autonomous manner. However, most employees are still facing restrictions to access data or simply do not have the right competence to work with data hindering any value creation. In that context, data democratization consists in deploying the right resources to foster data use in enterprise.
What is Data Democratization?
Data democratization is the enterprise’s capability to motivate and empower a wider range of employees - not just data experts - to understand, find, access, use, and share data in a secure and compliant way.
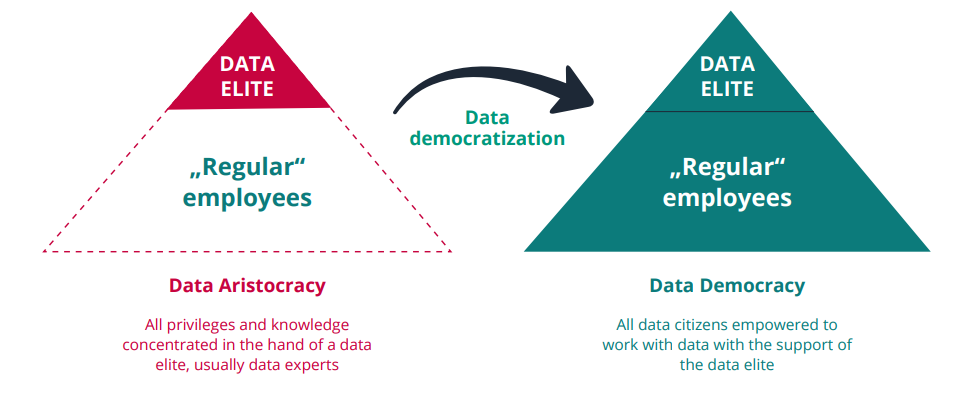
How can we address data democratization?
The concept of democratizing data is often confused with universal access to data, whereas it entails instead an organizational-wide cultural shift and teaching this wider range of employees with data from their own functional position or domain to contribute to business value creation, to scale data and AI for innovation.
The CC CDQ identified five important enablers leveraged as part of data democratization initiatives. While these 5 pillars can be built up without sequential necessity, they provide the roadmap to move forward, and addressing them all intentionally can help managers to successfully bring data to all corners of the organization.
5 pillars of Data Democratization
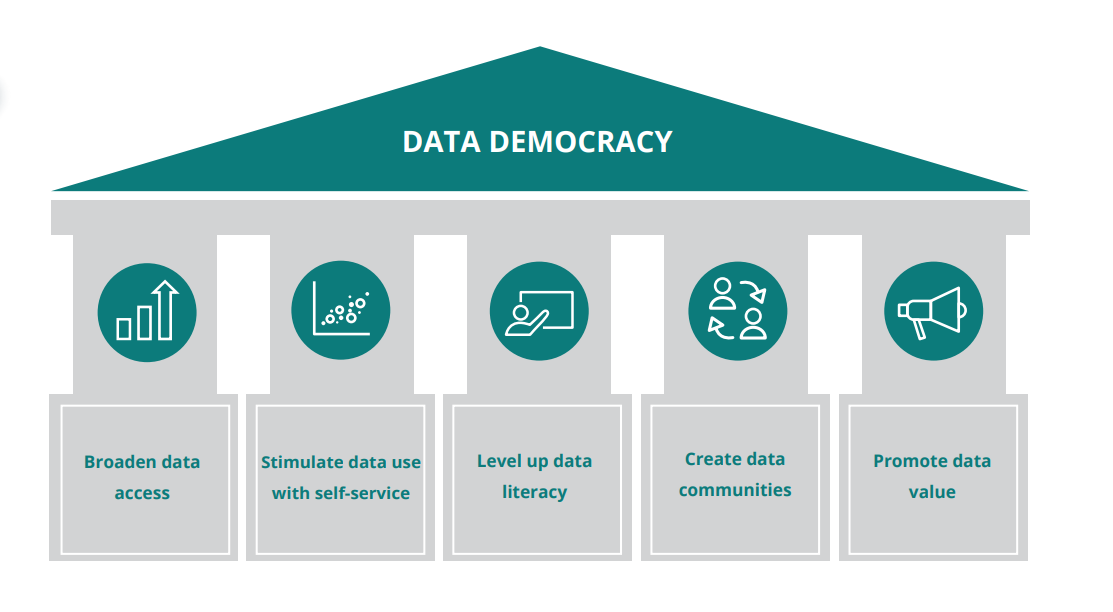
- Broader data access
Ensure that data users have access to one central and documented source of truth. Data Catalogues should be used as a privileged platform to break down silos and foster trust in data.
- Self-service analytics tools
Implement self-service analytics tools such as Tableau, MicroStrategy, PowerBI and Alteryx which are essential to stimulate insights generation from anywhere in the organization and to reduce the burden on analytics specialists
- Development of data and analytic skills
Foster data literacy by setting up training programmes that provide a broader audience (e.g. various personas) with the skills needed to find, access and use data. Encourage try-and-learn on analytics experimentation platforms while ensuring expert coaching.
- Collaboration and knowledge sharing
Establish both formal and informal mechanisms (e.g., project boards, data communities, conferences) to connect data specialists and non-specialists across various departments or business lines. Ensure shared understanding around data products request processes and easy discovery of existing knowledge (e.g., reports) to avoid duplication.
- Promotion of data value
Use corporate channels (e.g., conference, newsletter, podcast) to communicate key messages about the #businessvalue of data in your organization. Identify ambassadors or advocacy champions for data in business to stimulate demand for data and spread awareness.
Do you have any questions on Data Democratization?
Our data management experts are happy to help you and answer your questions.
