Business Partner Master Data
Customers and Vendors: the crucial master data domain in any successful business
Why is business partner master data domain so important?
Nearly every business process involves entities encompassed in the business partner domain, such as client dealings, supply sourcing, and customer relations. Efficient management of customers, vendors and suppliers streamlines operations, enhances customer relationships, strengthens supply chain functions, and drives overall growth.
(KYC, KYV)
Managing master data in the business partner domain enables companies to consolidate all relevant data and to gain a deep understanding of connections with customers, suppliers, and partners. Holistic view enhances decision-making and customer service quality, plus gives businesses an edge during negotiations or agreement renewals.
Business Partner Master Data Management
Many questions arise regarding precise definition of a business partner. While SAP environment provides a clear data structure, the concept of a business partner itself may pose difficulties for organizations, particularly when it comes to understanding what qualifies it as a customer. This crucial question (e.g. sales reporting can exhibit significant variations depending on the chosen definition) unravels complexities within the realm of business partner data management.
Business partners in SAP landscape powered by CDQ
For SAP Master Data Governance users Business Partner becomes the central master data object. SAP integrates the roles of customer, supplier, and employee to enable a smoother process automation. This is crucial as many companies often serve both as suppliers and customers. The SAP Business Partner ensures data consistency by assigning the relevant roles to the same master data object.
CDQ empowers SAP users with seamless integration* of Business Partner Lookup to make business partner onboarding and maintenance a risk-free, user-friendly process - paving a sustainable way to improve business partner data quality in SAP.
Our SAP-certified First Time Right solution pulls in business partner information from more than 70 external sources, normalizes it to SAP One Domain Model Business Partner, and guarantees top-notch data quality using AI and more than 2,500 ready-to-use data quality rules.
While many companies spend months defining the business partner concept, our experts from CDQ Business Consulting
can help you establish a clear scope of the project and support your teams at all stages of implementation.
Business partner master data changes
The volatile business landscape is subject to constant changes. Your suppliers, vendors and customers may have moved to a new location, or you may want to change the payment terms.
Without a sustainable approach to keeping your business partner master data up to date, your business is exposed to a range of risks:
- When credit assessments miss the mark or financial data lags behind, the danger of partnering with insolvent entities rises, potentially resulting in significant financial setbacks.
- Falling short on meeting regulatory standards, whether it's anti-money laundering mandates or tax regulations, can lead to severe penalties and legal ramifications.
- With weak data governance or insufficient security measures, your sensitive business partner information becomes vulnerable to unauthorized access or cyber threats, jeopardizing your company's integrity.
Your cloud solutions for collaborative business partner data management
Collaborative management of business partner master data
Business partner master data encompasses essential attributes such as legal names, addresses, tax identification numbers, and assessments of financial stability and social compliance - details directly reflecting the real-world status of your business partners.
An analysis conducted by CC CDQ found that among large multinational enterprises, an overlap in the business partner master data domain ranges between 40% to 60%, depending on the industry.
This is where collaborative data management steps in: by jointly managing common data, quality rules, and external sources, companies can significantly reduce workload and simultaneously enhance the quality of business partner data.
The untapped potential of your business partner data
Managing business partner master data manually poses numerous challenges that can impede
organizational efficiency and hinder growth. Manual processes are inherently time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to scale, particularly as businesses expand and generate larger volumes of data.
From accelerating data entry and validation to enforcing compliance and minimizing errors, automation empowers organizations to realize significant financial benefits while laying the foundation for sustainable growth, AI-readiness, and competitive edge.

Turn your business partner master data into golden records with CDQ
Powered by SAP, we have pioneered the Golden Record concept, a method that consolidates data from multiple sources into a single, complete and trustworthy business partner record. By simultaneously validating business partners against over 70 external data sources, including premium CDQ Data Sharing Pool with over 2 million business partners, you can seamlessly augment your business partners into solid Golden Records upon creation or change.
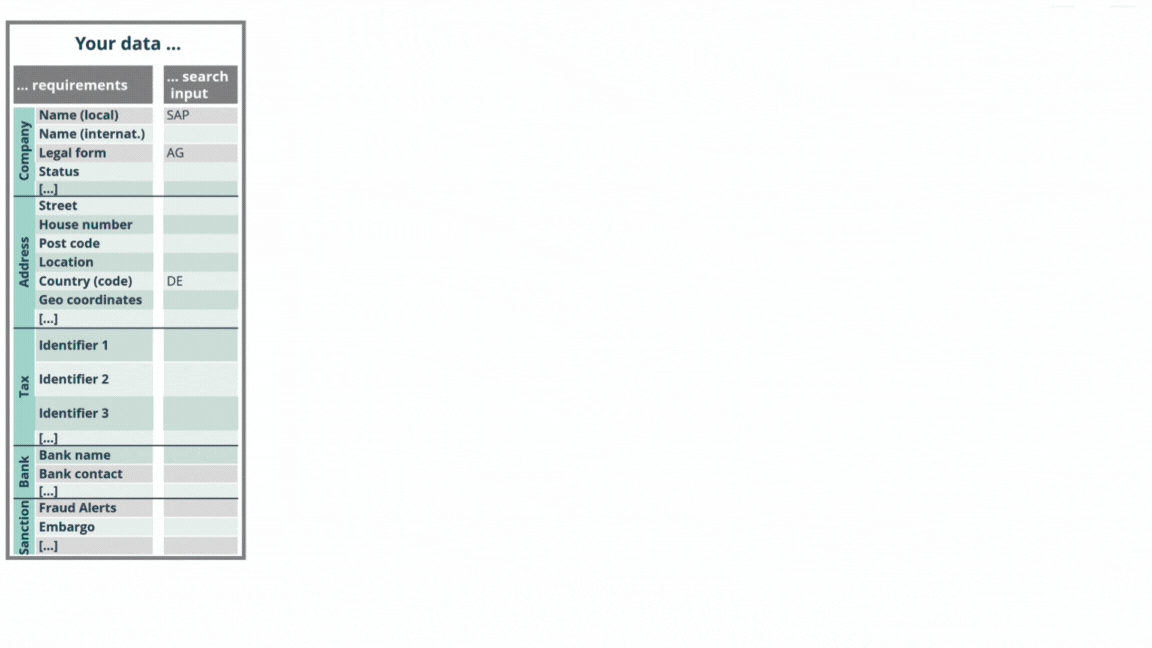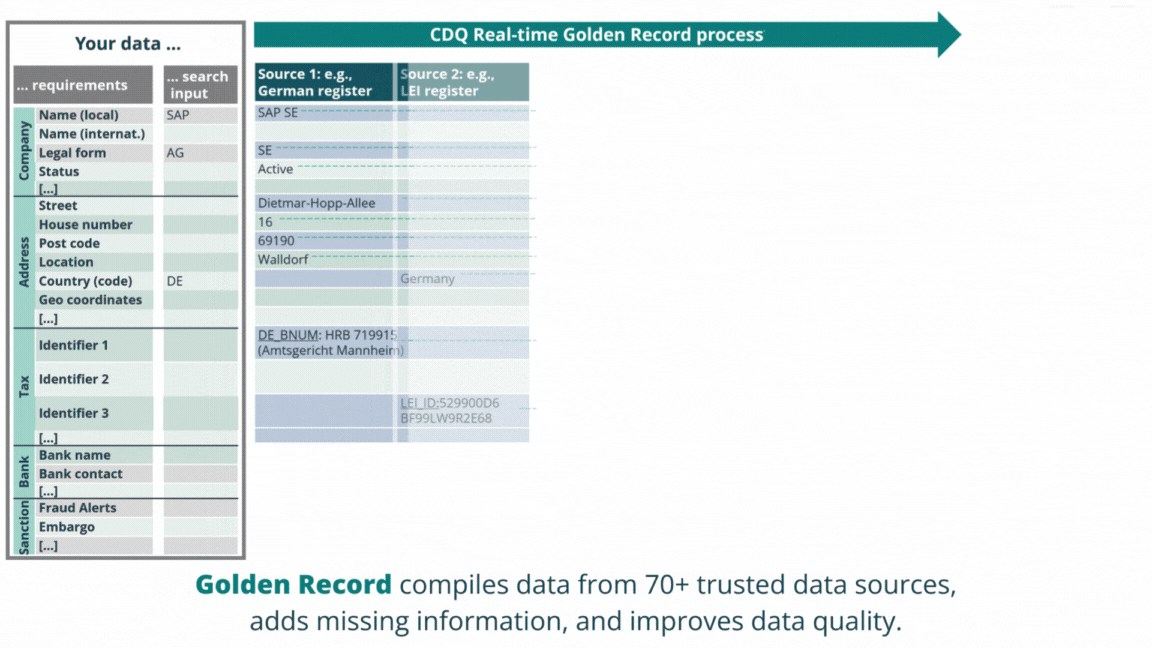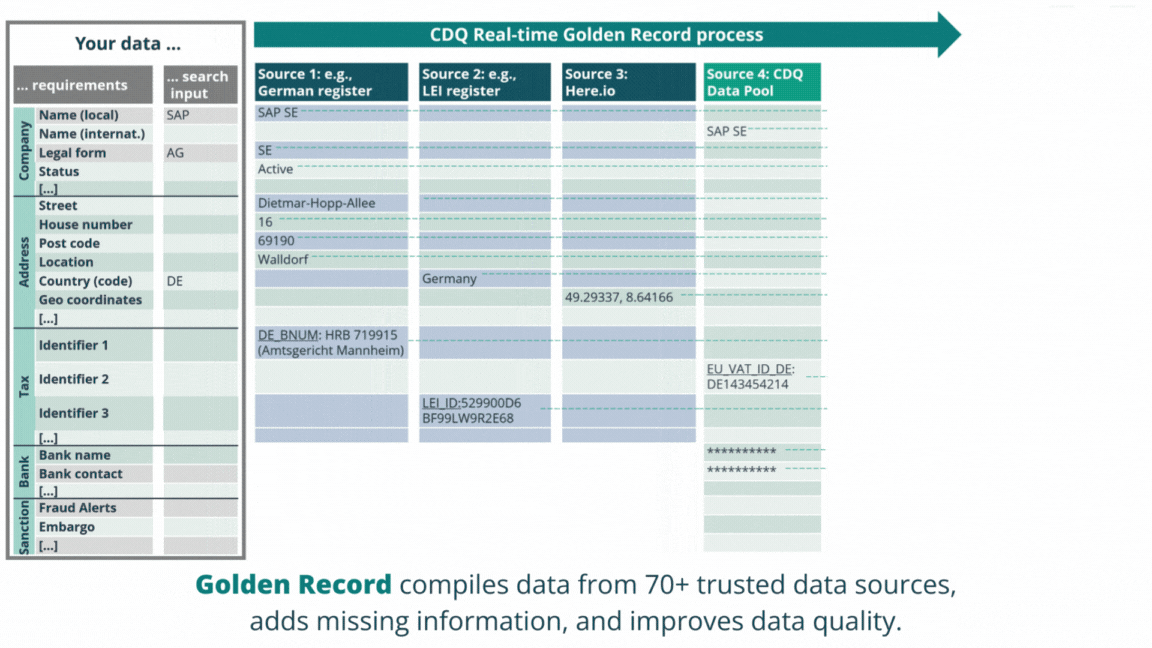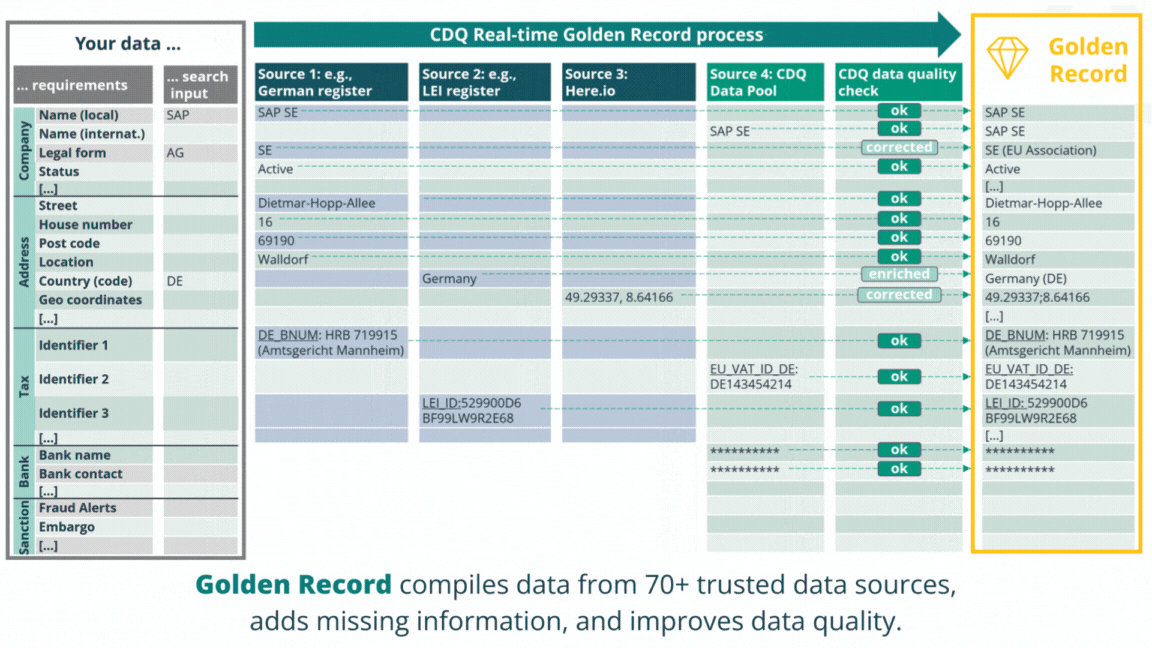
Boost your master data management with clean data
The quality and accuracy of data in the business partner domain are critical for ensuring smooth business operations. Errors or discrepancies can lead to customer dissatisfaction, supplier disputes, and regulatory compliance issues.
To maintain high data quality in the business partner domain, effective data management strategies involve implementing robust data governance structures, advanced analytics, and innovative technology solutions.
With CDQ you can facilitate a smooth and productive business ecosystem: beneficial for promoting customer satisfaction, fostering positive supplier relationships, and ensuring strict adherence to regulatory norms.
Over 200 million data records in the Data Sharing Pool, powered by more than 2,500 data quality rules and 70+ trusted data sources guard your business partners quality and accuracy.
Business partner master data
What is business partner master data, and why is it important for organizations?
Business partner master data refers to the comprehensive and structured information about entities that an organization interacts with, including customers, vendors, suppliers, and other business partners. It encompasses details such as contact information, addresses, financial records, and relationship hierarchies. Managing this data effectively is crucial for organizations to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and maintain strong relationships with stakeholders.
What types of information are typically included in business partner master data?
Common types of information found in business partner master data include:
- Name and legal entity information
- Contact details (address, phone number, email)
- Financial information (payment terms, credit limits)
- Relationship hierarchy (parent-child relationships)
- Business classifications (customer, vendor, supplier)
- Historical transaction data
How do organizations ensure the quality and accuracy of business partner master data?
Organizations employ various strategies to maintain the quality and accuracy of business partner master data, including data validation checks, regular audits, data cleansing processes, and establishing data governance policies. Additionally, implementing data stewardship roles and leveraging data quality tools can help continuously monitor and improve data integrity.
What are the common challenges of managing business partner master data?
Typical challenges include data inconsistency across systems, data duplication, incomplete or outdated information, and difficulties in integrating data from disparate sources. Managing changes in business relationships and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations are also significant challenges.
What are the best practices for creating and maintaining business partner master data?
Best practices include establishing clear data governance policies, enforcing standardized data entry procedures, implementing data quality controls, conducting regular data audits, and fostering collaboration between business and IT stakeholders. Additionally, investing in robust master data management (MDM) solutions can streamline data management processes.
How do organizations handle data governance and compliance requirements related to business partner master data?
Organizations establish data governance frameworks to define roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing business partner master data. Compliance with data privacy regulations such as GDPR or CCPA involves implementing data protection measures, obtaining consent for data collection, and ensuring secure data handling practices.
What technologies or tools are commonly used for managing business partner master data?
Commonly used technologies include Master Data Management (MDM) systems, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, and data quality tools. These tools facilitate data integration, cleansing, deduplication, and governance processes to ensure the accuracy and consistency of business partner master data.
How does effective management of business partner master data contribute to overall business performance and decision-making?
Effective management of business partner master data enables organizations to gain insights into customer behavior, optimize supply chain processes, mitigate risks, and identify growth opportunities. Accurate and up-to-date master data enhances operational efficiency, supports strategic planning, and enables informed decision-making across all business functions.
